Blockchain Technology
Dictionary.com,defines Blockchain Technology as a digital ledger in which transactions made in bitcoin or another cryptocurrency are recorded chronologically and publicly.
Blockchain Technology is very likely the foundation of a new internet. It provides a level of integrity we have never seen on the internet before. Data copied or stored in any one location makes it vulnerable to compromise or hacking. Blockchain data is shared by several thousand computers called nodes. It is encrypted, duplicated and distributed using a spreadsheet type format. Every 10 minutes it updates itself keeping it safe from hackers.
Blockchain Technology History
In 2008 a person or group of people called Satashi Nakamoto designed Blockchain Technology for digital currency like Bitcoin. Implemented in 2009, the system has morphed into something much larger than anyone imagined. Financial transactions and legal documents are the next focus markets. The possibilities for future applications are endless.
Blockchain Technology Data Flow
The following diagram, courtesy of blockgeeks.com., is a great example of how the Blockchain Technology data works.
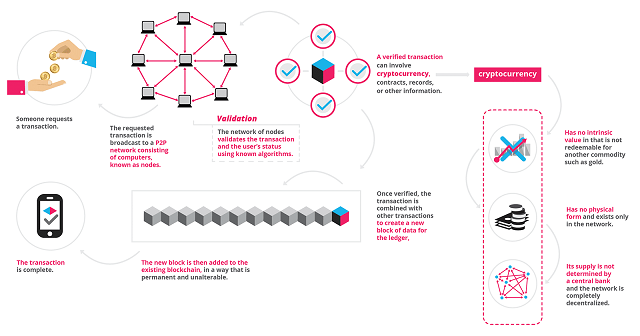
By duplicating and sharing the data, it cannot be manipulated or controlled by any one person or thing. Each block contains data in its current form. Data can only be changed when and only when the validation criteria is met.
Blockchain Example
Imagine your the car title as blockchain technology data and duplicated several thousand times. Most people own their vehicle for several years. The car title data is sitting there. Updated every 10 minutes for as long as you own your car. The title data is safe. You would have to change several thousand duplicates in order compromise the data. Validation points and encryption protect it. One day you sell your car to a new owner. The system recognizes you as part of the validation process (a node). A new blockchain is added. The new owner is now part of that validation process (a node).
Data Security
Blockchain technology stores its data across its network of computers or nodes, eliminating the risk of keeping data in one central location. Every node is an “administrator” of the blockchain, and joins the network voluntarily.
The weakness of data storage is a single central point of entry. Decentralized data is the key to Blockchain technology. To corrupt or steal data is impossible. The latest example of hackers compromising sensitive data we all heard about was Experian. Their central data security was no match for the hackers. The hackers are outpacing the security measures implemented to keep them out. If Experian had blockchain technology there is no way the hackers would have been successful.
Major Security Points
- No control by any single entity.
- Has no single point of failure.
- Transparency is embedded within the nodes network. By definition it is public.
- Altering any unit of information on the blockchain would mean using a huge amount of computing power to override the entire network.

